基于 Android 7.1.1 源码分析,本文为原创,转载请说明出处。。。
0 前言
JobSchedulerService 服务的启动,是在 SystemServer 的 startOtherServices 方法中:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9private void startOtherServices() {
...
mSystemServiceManager.startService(JobSchedulerService.class);
...
}
这个方法首先会调用服务的 Constructer,然后调用服务的 onStart 方法!
同时,在 ActivityManagerService.systemReady 方法中,会调用如下的方法:
1 | // 启动当前的设备用户! |
该方法的细节如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public void startUser(final int userHandle) {
final int serviceLen = mServices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < serviceLen; i++) {
final SystemService service = mServices.get(i);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "onStartUser "
+ service.getClass().getName());
try {
// 拉起所有 SystemService 的子类的 onStartUser 方法!
service.onStartUser(userHandle);
} catch (Exception ex) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Failure reporting start of user " + userHandle
+ " to service " + service.getClass().getName(), ex);
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
1 JobSchedulerService
我们先来看 JobSchedulerService 的构造器:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public JobSchedulerService(Context context) {
super(context);
// 创建主线程的 looper,创建对应的 Handler
mHandler = new JobHandler(context.getMainLooper());
mConstants = new Constants(mHandler);
// 创建 binder 服务端
mJobSchedulerStub = new JobSchedulerStub();
// 初始化 JobStore 对象!
mJobs = JobStore.initAndGet(this);
// Create the controllers.
mControllers = new ArrayList<StateController>();
mControllers.add(ConnectivityController.get(this));
mControllers.add(TimeController.get(this));
mControllers.add(IdleController.get(this));
mControllers.add(BatteryController.get(this));
mControllers.add(AppIdleController.get(this));
mControllers.add(ContentObserverController.get(this));
mControllers.add(DeviceIdleJobsController.get(this));
}
这里构造器其中,创建了一些很重要的成员变量,其中多个控制器:
ConnectivityController:用于监听网络连接状态的广播;DeviceIdleJobsController:ContentObserverController:用于监听数据库的变化;AppIdleController:用于监听app是否处于空闲状态;BatteryController:用于监听电池是否充电,电量状态的广播;IdleController:用于监听屏幕亮 / 灭,进入 / 退出睡眠,状态改变的广播;TimeController:用于监听 job 时间范围的广播;
下图展示了 这几个主要的 Controller 之间的关系:
(图先省略啦,后续补上,哈哈)
可以看到,他们都继承了 StateController 类,我们后面来分析控制器!
1.1 JobStore
JobStore 方法的作用是存储了管理系统中存储的所有注册过的 JobStore:
1 | public class JobStore { |
上面是 JobStore 的初始化操作,该方法会创建 job 目录以及 jobs.xml 文件, 以及从文件中读取所有的 JobStatus。
1.1.1 readJobMapFromDisk
这个方法创建了一个 Runnable 去实现具体的业务!1
2
3
4
public void readJobMapFromDisk(JobSet jobSet) {
new ReadJobMapFromDiskRunnable(jobSet).run();
}
从 Jobs.xml 文件中读取数据:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40private class ReadJobMapFromDiskRunnable implements Runnable {
private final JobSet jobSet;
/**
* @param jobSet Reference to the (empty) set of JobStatus objects that back the JobStore,
* so that after disk read we can populate it directly.
*/
ReadJobMapFromDiskRunnable(JobSet jobSet) {
this.jobSet = jobSet;
}
public void run() {
try {
List<JobStatus> jobs;
FileInputStream fis = mJobsFile.openRead();
synchronized (mLock) {
jobs = readJobMapImpl(fis);
if (jobs != null) {
for (int i=0; i<jobs.size(); i++) {
this.jobSet.add(jobs.get(i));
}
}
}
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
if (JobSchedulerService.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Could not find jobs file, probably there was nothing to load.");
}
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
if (JobSchedulerService.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error parsing xml.", e);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (JobSchedulerService.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error parsing xml.", e);
}
}
}
... ... ... ...
}
可以看出,调用了 readJobMapImpl 方法来解析 Jobs.xml !
1.1.2 readJobMapImpl
1 | private List<JobStatus> readJobMapImpl(FileInputStream fis) |
这里是通过循环处理 jobs.xml 文件中的标签
1.1.3 restoreJobFromXml
这个方法负责解析每个JobStatus。
注意这里只有重启设备后需要保留的 Job,才会写入 jobs.xml 文件中,即:这个 Job 是 isPersisted 的!!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139private JobStatus restoreJobFromXml(XmlPullParser parser) throws XmlPullParserException,
IOException {
JobInfo.Builder jobBuilder;
int uid, sourceUserId;
try {
jobBuilder = buildBuilderFromXml(parser);
jobBuilder.setPersisted(true);
// 解析基本信息: uid、priority、flags 和 sourceUserId !
uid = Integer.parseInt(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "uid"));
String val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "priority");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setPriority(Integer.parseInt(val));
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "flags");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setFlags(Integer.parseInt(val));
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "sourceUserId");
sourceUserId = val == null ? -1 : Integer.parseInt(val);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Error parsing job's required fields, skipping");
return null;
}
// 解析获得 sourcePackageName 和 sourceTag!
String sourcePackageName = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "sourcePackageName");
final String sourceTag = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "sourceTag");
int eventType;
// Read out constraints tag.
do {
eventType = parser.next();
} while (eventType == XmlPullParser.TEXT); // Push through to next START_TAG.
if (!(eventType == XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
XML_TAG_PARAMS_CONSTRAINTS.equals(parser.getName()))) {
// Expecting a <constraints> start tag.
return null;
}
try {
buildConstraintsFromXml(jobBuilder, parser);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error reading constraints, skipping.");
return null;
}
parser.next(); // Consume </constraints>
// Read out execution parameters tag.
do {
eventType = parser.next();
} while (eventType == XmlPullParser.TEXT);
if (eventType != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
return null;
}
// Tuple of (earliest runtime, latest runtime) in elapsed realtime after disk load.
Pair<Long, Long> elapsedRuntimes;
try {
elapsedRuntimes = buildExecutionTimesFromXml(parser);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error parsing execution time parameters, skipping.");
}
return null;
}
final long elapsedNow = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
if (XML_TAG_PERIODIC.equals(parser.getName())) {
try {
String val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "period");
final long periodMillis = Long.valueOf(val);
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "flex");
final long flexMillis = (val != null) ? Long.valueOf(val) : periodMillis;
jobBuilder.setPeriodic(periodMillis, flexMillis);
// As a sanity check, cap the recreated run time to be no later than flex+period
// from now. This is the latest the periodic could be pushed out. This could
// happen if the periodic ran early (at flex time before period), and then the
// device rebooted.
if (elapsedRuntimes.second > elapsedNow + periodMillis + flexMillis) {
final long clampedLateRuntimeElapsed = elapsedNow + flexMillis
+ periodMillis;
final long clampedEarlyRuntimeElapsed = clampedLateRuntimeElapsed
- flexMillis;
... ... ... ...
elapsedRuntimes =
Pair.create(clampedEarlyRuntimeElapsed, clampedLateRuntimeElapsed);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error reading periodic execution criteria, skipping.");
return null;
}
} else if (XML_TAG_ONEOFF.equals(parser.getName())) {
try {
if (elapsedRuntimes.first != JobStatus.NO_EARLIEST_RUNTIME) {
jobBuilder.setMinimumLatency(elapsedRuntimes.first - elapsedNow);
}
if (elapsedRuntimes.second != JobStatus.NO_LATEST_RUNTIME) {
jobBuilder.setOverrideDeadline(
elapsedRuntimes.second - elapsedNow);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error reading job execution criteria, skipping.");
return null;
}
} else {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Invalid parameter tag, skipping - " + parser.getName());
}
// Expecting a parameters start tag.
return null;
}
maybeBuildBackoffPolicyFromXml(jobBuilder, parser);
parser.nextTag(); // Consume parameters end tag.
// Read out extras Bundle.
do {
eventType = parser.next();
} while (eventType == XmlPullParser.TEXT);
if (!(eventType == XmlPullParser.START_TAG
&& XML_TAG_EXTRAS.equals(parser.getName()))) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Error reading extras, skipping.");
}
return null;
}
PersistableBundle extras = PersistableBundle.restoreFromXml(parser);
jobBuilder.setExtras(extras);
parser.nextTag(); // Consume </extras>
// Migrate sync jobs forward from earlier, incomplete representation
if ("android".equals(sourcePackageName)
&& extras != null
&& extras.getBoolean("SyncManagerJob", false)) {
sourcePackageName = extras.getString("owningPackage", sourcePackageName);
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Fixing up sync job source package name from 'android' to '"
+ sourcePackageName + "'");
}
}
// And now we're done
JobStatus js = new JobStatus(
jobBuilder.build(), uid, sourcePackageName, sourceUserId, sourceTag,
elapsedRuntimes.first, elapsedRuntimes.second);
return js;
}
这里面以后很多的细节,继续看:
1.1.3.1 buildBuilderFromXml
用来创建 JobInfo:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8private JobInfo.Builder buildBuilderFromXml(XmlPullParser parser) throws NumberFormatException {
// Pull out required fields from <job> attributes.
int jobId = Integer.parseInt(parser.getAttributeValue(null, "jobid"));
String packageName = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "package");
String className = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "class");
ComponentName cname = new ComponentName(packageName, className);
return new JobInfo.Builder(jobId, cname);
}
这里使用了建造者模式:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37public static final class Builder {
private final int mJobId;
private final ComponentName mJobService;
private PersistableBundle mExtras = PersistableBundle.EMPTY;
private int mPriority = PRIORITY_DEFAULT;
private int mFlags;
// Requirements.
private boolean mRequiresCharging;
private boolean mRequiresDeviceIdle;
private int mNetworkType;
private ArrayList<TriggerContentUri> mTriggerContentUris;
private long mTriggerContentUpdateDelay = -1;
private long mTriggerContentMaxDelay = -1;
private boolean mIsPersisted;
// One-off parameters.
private long mMinLatencyMillis;
private long mMaxExecutionDelayMillis;
// Periodic parameters.
private boolean mIsPeriodic;
private boolean mHasEarlyConstraint;
private boolean mHasLateConstraint;
private long mIntervalMillis;
private long mFlexMillis;
// Back-off parameters.
private long mInitialBackoffMillis = DEFAULT_INITIAL_BACKOFF_MILLIS;
private int mBackoffPolicy = DEFAULT_BACKOFF_POLICY;
/** Easy way to track whether the client has tried to set a back-off policy. */
private boolean mBackoffPolicySet = false;
public Builder(int jobId, ComponentName jobService) {
mJobService = jobService;
mJobId = jobId;
}
... ... ... ...
}
返回了 JobInfo 的内部类 Builder 的对象!
1.1.3.2 buildConstraintsFromXml
传入参数:JobInfo.Buidlder 和 XmlPullParser :1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22private void buildConstraintsFromXml(JobInfo.Builder jobBuilder, XmlPullParser parser) {
String val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "connectivity");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setRequiredNetworkType(JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_ANY);
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "unmetered");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setRequiredNetworkType(JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_UNMETERED);
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "not-roaming");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setRequiredNetworkType(JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_NOT_ROAMING);
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "idle");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setRequiresDeviceIdle(true);
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "charging");
if (val != null) {
jobBuilder.setRequiresCharging(true);
}
}
显然,这个方法也很简单,解析剩下的参数!
1.1.3.3 buildExecutionTimesFromXml
计算这个 Job 的最早运行时间和最晚的结束时间:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 private Pair<Long, Long> buildExecutionTimesFromXml(XmlPullParser parser)
throws NumberFormatException {
// Pull out execution time data.
final long nowWallclock = System.currentTimeMillis();
final long nowElapsed = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
long earliestRunTimeElapsed = JobStatus.NO_EARLIEST_RUNTIME;
long latestRunTimeElapsed = JobStatus.NO_LATEST_RUNTIME;
String val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "deadline");
if (val != null) {
long latestRuntimeWallclock = Long.valueOf(val);
long maxDelayElapsed =
Math.max(latestRuntimeWallclock - nowWallclock, 0);
latestRunTimeElapsed = nowElapsed + maxDelayElapsed;
}
val = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "delay");
if (val != null) {
long earliestRuntimeWallclock = Long.valueOf(val);
long minDelayElapsed =
Math.max(earliestRuntimeWallclock - nowWallclock, 0);
earliestRunTimeElapsed = nowElapsed + minDelayElapsed;
}
return Pair.create(earliestRunTimeElapsed, latestRunTimeElapsed);
}
}
接着来看:
1.1.3.4 maybeBuildBackoffPolicyFromXml
1 | private void maybeBuildBackoffPolicyFromXml(JobInfo.Builder jobBuilder, XmlPullParser parser) { |
接着:
1.1.3.5 PersistableBundle.restoreFromXml
1 | /** @hide */ |
接着:
1.1.3.6 JobInfo.buidler.build
根据解析的结果,创建 JobInfo 对象,这里调用了 JobInfo.buidler 的 build 方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60... ... ... ...
public JobInfo build() {
// Allow jobs with no constraints - What am I, a database?
if (!mHasEarlyConstraint && !mHasLateConstraint && !mRequiresCharging &&
!mRequiresDeviceIdle && mNetworkType == NETWORK_TYPE_NONE &&
mTriggerContentUris == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You're trying to build a job with no " +
"constraints, this is not allowed.");
}
mExtras = new PersistableBundle(mExtras); // Make our own copy.
// Check that a deadline was not set on a periodic job.
if (mIsPeriodic && (mMaxExecutionDelayMillis != 0L)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't call setOverrideDeadline() on a " +
"periodic job.");
}
if (mIsPeriodic && (mMinLatencyMillis != 0L)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't call setMinimumLatency() on a " +
"periodic job");
}
if (mIsPeriodic && (mTriggerContentUris != null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't call addTriggerContentUri() on a " +
"periodic job");
}
if (mIsPersisted && (mTriggerContentUris != null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't call addTriggerContentUri() on a " +
"persisted job");
}
if (mBackoffPolicySet && mRequiresDeviceIdle) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("An idle mode job will not respect any" +
" back-off policy, so calling setBackoffCriteria with" +
" setRequiresDeviceIdle is an error.");
}
JobInfo job = new JobInfo(this);
if (job.isPeriodic()) {
if (job.intervalMillis != job.getIntervalMillis()) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Specified interval for ")
.append(String.valueOf(mJobId))
.append(" is ");
formatDuration(mIntervalMillis, builder);
builder.append(". Clamped to ");
formatDuration(job.getIntervalMillis(), builder);
Log.w(TAG, builder.toString());
}
if (job.flexMillis != job.getFlexMillis()) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Specified flex for ")
.append(String.valueOf(mJobId))
.append(" is ");
formatDuration(mFlexMillis, builder);
builder.append(". Clamped to ");
formatDuration(job.getFlexMillis(), builder);
Log.w(TAG, builder.toString());
}
}
return job;
}
... ... ... ...
这里返回了 JobInfo 对象!
1.1.3.7 new JobStatus
最后,根据创建的 JobInfo 对象和前面的解析结果,创建 JobStatus 对象!1
2
3
4
5public JobStatus(JobInfo job, int callingUid, String sourcePackageName, int sourceUserId,
String sourceTag, long earliestRunTimeElapsedMillis, long latestRunTimeElapsedMillis) {
this(job, callingUid, sourcePackageName, sourceUserId, sourceTag, 0,
earliestRunTimeElapsedMillis, latestRunTimeElapsedMillis);
}
这个构造器调用了下面这个:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59private JobStatus(JobInfo job, int callingUid, String sourcePackageName,
int sourceUserId, String tag, int numFailures, long earliestRunTimeElapsedMillis,
long latestRunTimeElapsedMillis) {
this.job = job;
this.callingUid = callingUid;
int tempSourceUid = -1;
if (sourceUserId != -1 && sourcePackageName != null) {
try {
tempSourceUid = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().getPackageUid(sourcePackageName, 0,
sourceUserId);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Can't happen, PackageManager runs in the same process.
}
}
if (tempSourceUid == -1) {
this.sourceUid = callingUid;
this.sourceUserId = UserHandle.getUserId(callingUid);
this.sourcePackageName = job.getService().getPackageName();
this.sourceTag = null;
} else {
this.sourceUid = tempSourceUid;
this.sourceUserId = sourceUserId;
this.sourcePackageName = sourcePackageName;
this.sourceTag = tag;
}
this.batteryName = this.sourceTag != null
? this.sourceTag + ":" + job.getService().getPackageName()
: job.getService().flattenToShortString();
this.tag = "*job*/" + this.batteryName;
this.earliestRunTimeElapsedMillis = earliestRunTimeElapsedMillis;
this.latestRunTimeElapsedMillis = latestRunTimeElapsedMillis;
this.numFailures = numFailures;
int requiredConstraints = 0;
if (job.getNetworkType() == JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_ANY) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_CONNECTIVITY;
}
if (job.getNetworkType() == JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_UNMETERED) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_UNMETERED;
}
if (job.getNetworkType() == JobInfo.NETWORK_TYPE_NOT_ROAMING) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_NOT_ROAMING;
}
if (job.isRequireCharging()) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_CHARGING;
}
if (earliestRunTimeElapsedMillis != NO_EARLIEST_RUNTIME) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_TIMING_DELAY;
}
if (latestRunTimeElapsedMillis != NO_LATEST_RUNTIME) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_DEADLINE;
}
if (job.isRequireDeviceIdle()) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_IDLE;
}
if (job.getTriggerContentUris() != null) {
requiredConstraints |= CONSTRAINT_CONTENT_TRIGGER;
}
this.requiredConstraints = requiredConstraints;
}
暂时看到这里!
1.2 JobHandler
接下来,我们来看看 JobHander 的消息处理:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58private class JobHandler extends Handler {
public JobHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
public void handleMessage(Message message) {
synchronized (mLock) {
// 在系统刚刚启动的时候,mReadyToRock 的值为 false,当系统启动到 phase 600,则 mReadyToRock=true.
if (!mReadyToRock) {
return;
}
}
switch (message.what) {
case MSG_JOB_EXPIRED:
synchronized (mLock) {
JobStatus runNow = (JobStatus) message.obj;
// runNow can be null, which is a controller's way of indicating that its
// state is such that all ready jobs should be run immediately.
if (runNow != null && !mPendingJobs.contains(runNow)
&& mJobs.containsJob(runNow)) {
mJobPackageTracker.notePending(runNow);
mPendingJobs.add(runNow);
}
queueReadyJobsForExecutionLockedH();
}
break;
case MSG_CHECK_JOB: // 检查任务
synchronized (mLock) {
if (mReportedActive) {
// if jobs are currently being run, queue all ready jobs for execution.
queueReadyJobsForExecutionLockedH();
} else {
// Check the list of jobs and run some of them if we feel inclined.
maybeQueueReadyJobsForExecutionLockedH();
}
}
break;
case MSG_CHECK_JOB_GREEDY:
synchronized (mLock) {
queueReadyJobsForExecutionLockedH();
}
break;
case MSG_STOP_JOB: // 停止任务
cancelJobImpl((JobStatus)message.obj, null);
break;
}
maybeRunPendingJobsH();
// Don't remove JOB_EXPIRED in case one came along while processing the queue.
removeMessages(MSG_CHECK_JOB);
}
... ... ... ...
private final ReadyJobQueueFunctor mReadyQueueFunctor = new ReadyJobQueueFunctor();
... ... ... ...
private final MaybeReadyJobQueueFunctor mMaybeQueueFunctor = new MaybeReadyJobQueueFunctor();
... ... ... ...
}
这里,我们省略了一些方法,以后再慢慢分析!
1.3 Controllers
对于控制器,后面会有单独的博文详细分析,这里我们先看看 ConnectivityController!!
1.3.1 ConnectivityController
我们先来看一个控制器 ConnectivityController,先来看看他的代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29public class ConnectivityController extends StateController implements
ConnectivityManager.OnNetworkActiveListener {
private static final String TAG = "JobScheduler.Conn";
private final ConnectivityManager mConnManager;
private final NetworkPolicyManager mNetPolicyManager;
private final ArrayList<JobStatus> mTrackedJobs = new ArrayList<JobStatus>();
/** Singleton. */
private static ConnectivityController mSingleton;
private static Object sCreationLock = new Object();
public static ConnectivityController get(JobSchedulerService jms) {
synchronized (sCreationLock) {
if (mSingleton == null) {
mSingleton = new ConnectivityController(jms, jms.getContext(), jms.getLock());
}
return mSingleton;
}
}
private ConnectivityController(StateChangedListener stateChangedListener, Context context,
Object lock) {
super(stateChangedListener, context, lock);
mConnManager = mContext.getSystemService(ConnectivityManager.class);
mNetPolicyManager = mContext.getSystemService(NetworkPolicyManager.class);
// 注册监听网络连接状态的广播,且采用 BackgroundThread 线程
final IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter(ConnectivityManager.CONNECTIVITY_ACTION);
mContext.registerReceiverAsUser(
mConnectivityReceiver, UserHandle.SYSTEM, intentFilter, null, null);
mNetPolicyManager.registerListener(mNetPolicyListener);
}
当监听到 CONNECTIVITY_ACTION 广播,onReceive 方法的执行位于 “android.bg” 线程。
其他的控制器很类似,我们在后面的文章中,会集中分析这些控制器!
1.4 JobSchedulerStub
JobSchedulerStub 继承了 IJobScheduler.Stub,作为 Binder 机制的服务端的桩对象,为 Binder 客户端提供服务!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47final class JobSchedulerStub extends IJobScheduler.Stub {
private final SparseArray<Boolean> mPersistCache = new SparseArray<Boolean>();
private void enforceValidJobRequest(int uid, JobInfo job) {
... ... ... ... ...
}
private boolean canPersistJobs(int pid, int uid) {
... ... ... ... ...
}
// IJobScheduler implementation
public int schedule(JobInfo job) throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
public int scheduleAsPackage(JobInfo job, String packageName, int userId, String tag)
throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
public List<JobInfo> getAllPendingJobs() throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
public JobInfo getPendingJob(int jobId) throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
public void cancelAll() throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
public void cancel(int jobId) throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
/**
* "dumpsys" infrastructure
*/
public void dump(FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter pw, String[] args) {
... ... ... ... ...
}
public void onShellCommand(FileDescriptor in, FileDescriptor out, FileDescriptor err,
String[] args, ResultReceiver resultReceiver) throws RemoteException {
... ... ... ... ...
}
};
我们简单的分析下上面的方法:
1.4.1 enforceValidJobRequest
当一个应用想通过 JobScheduler 来注册一个任务的时候,需要实现一个服务:JobService,当任务注册到 JobScheduler 后,JobScheduler 通过注册时,设置的条件,当满足条件时,就调用 onJobStart 方法拉起 JobService 来执行任务;当不满足条件,就调用 onJobStop 方法,挂起 JobService 来停止任务!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23private void enforceValidJobRequest(int uid, JobInfo job) {
final IPackageManager pm = AppGlobals.getPackageManager();
final ComponentName service = job.getService();
try {
ServiceInfo si = pm.getServiceInfo(service,
PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_AWARE
| PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_UNAWARE,
UserHandle.getUserId(uid));
if (si == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No such service " + service);
}
if (si.applicationInfo.uid != uid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("uid " + uid +
" cannot schedule job in " + service.getPackageName());
}
if (!JobService.PERMISSION_BIND.equals(si.permission)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Scheduled service " + service
+ " does not require android.permission.BIND_JOB_SERVICE permission");
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Can't happen; the Package Manager is in this same process
}
}
这个方法主要的作用是校验如下几项:
1、是否有这个 JobService,
2、JobService 的 uid 是否等于调用者的 uid,就是说,这个 JobService 是否属于这个应用!
2、JobService 是否在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中配置了相应的权限:
1.4.2 canPersistJobs
判断应用是否有 android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED 的权限,如果有这个权限的话,设备重启后,能够保留该应用的任务!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private boolean canPersistJobs(int pid, int uid) {
final boolean canPersist;
synchronized (mPersistCache) {
Boolean cached = mPersistCache.get(uid);
if (cached != null) {
canPersist = cached.booleanValue();
} else {
// Persisting jobs is tantamount to running at boot, so we permit
// it when the app has declared that it uses the RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED
// permission
int result = getContext().checkPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED, pid, uid);
canPersist = (result == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED);
mPersistCache.put(uid, canPersist);
}
}
return canPersist;
}
最终的结果会保存在 mPersistCache 集合中!
1.4.3 schedule
这个方法是我们最常用的,来注册Job的!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25// 我们是实际上调用的是这个方法!
public int schedule(JobInfo job) throws RemoteException {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Scheduling job: " + job.toString());
}
// 获得调用方的 pid 和 uid!
final int pid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
// 校验操作
enforceValidJobRequest(uid, job);
// 如果这个Job是重启后可保留的,检查权限!
if (job.isPersisted()) {
if (!canPersistJobs(pid, uid)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Error: requested job be persisted without"
+ " holding RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED permission.");
}
}
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return JobSchedulerService.this.schedule(job, uid);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
最后 调用服务端的 schedule 方法继续注册!
1.4.4 scheduleAsPackage
接下来,我们来看一个和 schedule 方法很类似的方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public int scheduleAsPackage(JobInfo job, String packageName, int userId, String tag)
throws RemoteException {
final int callerUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Caller uid " + callerUid + " scheduling job: " + job.toString()
+ " on behalf of " + packageName);
}
if (packageName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Must specify a package for scheduleAsPackage()");
}
int mayScheduleForOthers = getContext().checkCallingOrSelfPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.UPDATE_DEVICE_STATS);
if (mayScheduleForOthers != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
throw new SecurityException("Caller uid " + callerUid
+ " not permitted to schedule jobs for other apps");
}
if ((job.getFlags() & JobInfo.FLAG_WILL_BE_FOREGROUND) != 0) {
getContext().enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(
android.Manifest.permission.CONNECTIVITY_INTERNAL, TAG);
}
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return JobSchedulerService.this.scheduleAsPackage(job, callerUid,
packageName, userId, tag);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
最后 调用服务端的 scheduleAsPackage 方法继续注册!
1.4.5 getXXXPendingJobs
下面来看这两个方法:getAllPendingJobs:获得应用注册的所有的正在等待的 Job!getPendingJob:获得应用程序注册的 jobId 指定的正在等待的 Job!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public List<JobInfo> getAllPendingJobs() throws RemoteException {
final int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return JobSchedulerService.this.getPendingJobs(uid);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
public JobInfo getPendingJob(int jobId) throws RemoteException {
final int uid = Binder.getCallingUid();
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
return JobSchedulerService.this.getPendingJob(uid, jobId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
最后 调用服务端的 scheduleAsPackage 方法!
1.4.6 cancelXXX
接着是取消任务的相关方法:
cancelAll:取消应用注册的所有任务!cancel:取消jobId对应的任务!
1 |
|
最后分别调用的是客户端的 cancelJobForUid 方法和 cancelJob 方法!
1.4.7 dump
这个方法是用来为控制台 dumpsys 命令提供数据的:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public void dump(FileDescriptor fd, PrintWriter pw, String[] args) {
getContext().enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(android.Manifest.permission.DUMP, TAG);
long identityToken = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
JobSchedulerService.this.dumpInternal(pw, args);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identityToken);
}
}
接着看:
1.4.8 onShellCommand
1 |
|
2 onStart
在 onStart 方法中,又调用了如下的方法:1
2
3
4
5
public void onStart() {
publishLocalService(JobSchedulerInternal.class, new LocalService());
publishBinderService(Context.JOB_SCHEDULER_SERVICE, mJobSchedulerStub);
}
主要有两个作用:
- 公开本地服务:
LocalService,类型为JobSchedulerInternal.class,只能被系统进程访问。 - 公开
Binder通信服务,名称为:jobscheduler,服务的实体对象是:mJobSchedulerStub,实现了IJobScheduler.Stub接口,其实就是将JobSchedulerService自身注册进SystemManager中,是其能被其他服务和应用访问到!
接下来,我们一个一个来看:
2.1 publishLocalService
这个方法是继承自 SystemService 的:1
2
3protected final <T> void publishLocalService(Class<T> type, T service) {
LocalServices.addService(type, service);
}
调用了 LocalServices的静态方法,addService:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public final class LocalServices {
private LocalServices() {}
private static final ArrayMap<Class<?>, Object> sLocalServiceObjects =
new ArrayMap<Class<?>, Object>();
... ... ... ...
public static <T> void addService(Class<T> type, T service) {
synchronized (sLocalServiceObjects) {
if (sLocalServiceObjects.containsKey(type)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Overriding service registration");
}
sLocalServiceObjects.put(type, service);
}
}
... ... ... ...
}
接着来看:
2.2 publishBinderService
这个方法也是继承了 SystemServer 的方法:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service) {
publishBinderService(name, service, false);
}
protected final void publishBinderService(String name, IBinder service,
boolean allowIsolated) {
ServiceManager.addService(name, service, allowIsolated);
}
其实就是将自身加入到 SystemManager 中去!
3 onBootPhase
我们知道,设备在开机的时候,会处于不同的状态,在每个状态时,都要通知服务,服务会根据不同的状态,进行不同是开始初始化操作!!
3.1 SystemServiceM.startBootPhase
具体的调用在这里:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27public void startBootPhase(final int phase) {
if (phase <= mCurrentPhase) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Next phase must be larger than previous");
}
mCurrentPhase = phase;
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting phase " + mCurrentPhase);
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "OnBootPhase " + phase);
// 遍历所有的系统服务!
final int serviceLen = mServices.size();
for (int i = 0; i < serviceLen; i++) {
final SystemService service = mServices.get(i);
try {
//【1】调用服务的 onBootPhase 方法!
service.onBootPhase(mCurrentPhase);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to boot service "
+ service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onBootPhase threw an exception during phase "
+ mCurrentPhase, ex);
}
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
对于 JobSchedulerService 服务,他需要在如下的 2 个阶段进行初始化!1
2
3
4// 表示系统服务已经准备好了!
public static final int PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY = 500;
// 表示第三方应用已经可以启动了!
public static final int PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START = 600;
我们来看看 JobSchedulerService 在不同的状态下做了什么初始化:
3.2 JobSchedulerS.onBootPhase
1 |
|
这里的是根据开机的阶段,进行不同的初始化操作,这里我们来看看 JobServiceContext!
3.3 JobServiceContext
创建 JobServiceContext 对象,参数传递:
Context context:JobSchedulerService.getContext。Object lock:JobSchedulerService.getObject。IBatteryStats batteryStats:JobSchedulerService.mBatteryStats。JobPackageTracker tracker:JobSchedulerService.tracker。JobCompletedListener completedListener:JobSchedulerService,其本身实现了这个接口。Looper looper:getContext().getMainLooper(),JobSchedulerService所在主线程的Looper。
1 | JobServiceContext(JobSchedulerService service, IBatteryStats batteryStats, |
此处的 JobServiceHandler 绑定的是 system_server 进程的主线程。
3.3.1 JobServiceHandler
每一个 JobServiceContext 都有一个 JobServiceHandler 对象,JobSchedulerService 通过这个 handler 对象向 JSC 发送消息!1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59private class JobServiceHandler extends Handler {
JobServiceHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
public void handleMessage(Message message) {
switch (message.what) {
case MSG_SERVICE_BOUND: // 绑定 jobService 服务!
removeOpTimeOut();
handleServiceBoundH();
break;
case MSG_CALLBACK: // job 周期变化的回调!
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "MSG_CALLBACK of : " + mRunningJob
+ " v:" + VERB_STRINGS[mVerb]);
}
removeOpTimeOut();
if (mVerb == VERB_STARTING) {
final boolean workOngoing = message.arg2 == 1;
handleStartedH(workOngoing);
} else if (mVerb == VERB_EXECUTING ||
mVerb == VERB_STOPPING) {
final boolean reschedule = message.arg2 == 1;
handleFinishedH(reschedule);
} else {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Unrecognised callback: " + mRunningJob);
}
}
break;
case MSG_CANCEL: // 取消 job!
if (mVerb == VERB_FINISHED) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG,
"Trying to process cancel for torn-down context, ignoring.");
}
return;
}
mParams.setStopReason(message.arg1);
if (message.arg1 == JobParameters.REASON_PREEMPT) {
mPreferredUid = mRunningJob != null ? mRunningJob.getUid() :
NO_PREFERRED_UID;
}
handleCancelH();
break;
case MSG_TIMEOUT: // job 超时!
handleOpTimeoutH();
break;
case MSG_SHUTDOWN_EXECUTION:
closeAndCleanupJobH(true /* needsReschedule */);
break;
default:
Slog.e(TAG, "Unrecognised message: " + message);
}
}
... ... ... ... ...
}
对于 JobServiceHandler 的细节,我们在后续的分析中会详细介绍,这里就不多说了!
4 startUser
我们来看看 startUser 方法中的细节:
1 |
|
目的就是:为当前的用户执行 job!
5 总结
JSS.JobHandler:运行在system_server进程的主线程;JobServiceContext.JobServiceHandler:运行在system_server进程的主线程;JobSchedulerStub:作为实现接口IJobScheduler的binder服务端;JobStore:其成员变量mIoHandler运行在android.io线程;JobStatus:JSS从/data/system/job/jobs.xml文件中读取每个JobInfo,再解析成JobStatus对象,添加到mJobSet。
可见 JobSchedulerService 启动过程,最主要工作是从 jobs.xml 文件收集所有的需要重启保留的 jobs,放入到 JobStore 的成员变量 mJobSet。
我们来先简单的看看 JobSchedulerService 的类关系图:
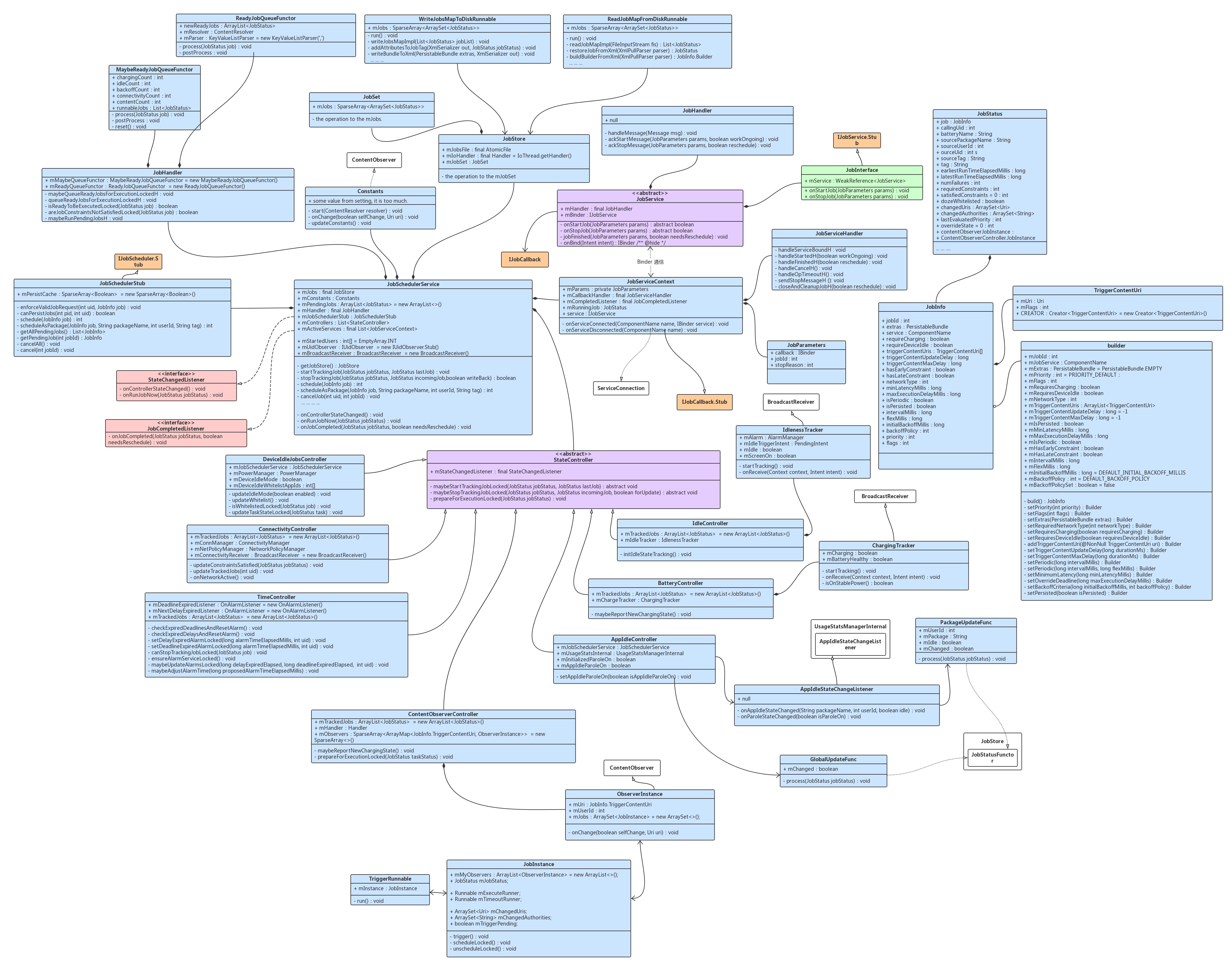
哈哈,是不是蒙圈了呢?后面我会陆续分析的,这一篇就到这里,累死我了!